Ameliorative effects of Tagetes lucida on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity, diabetic nephropathy and heat exposure in animal models
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36829/63CTS.v10i2.1385Keywords:
Aminoglycosides; hyperglycemia; dehydration, kidney, in vivoAbstract
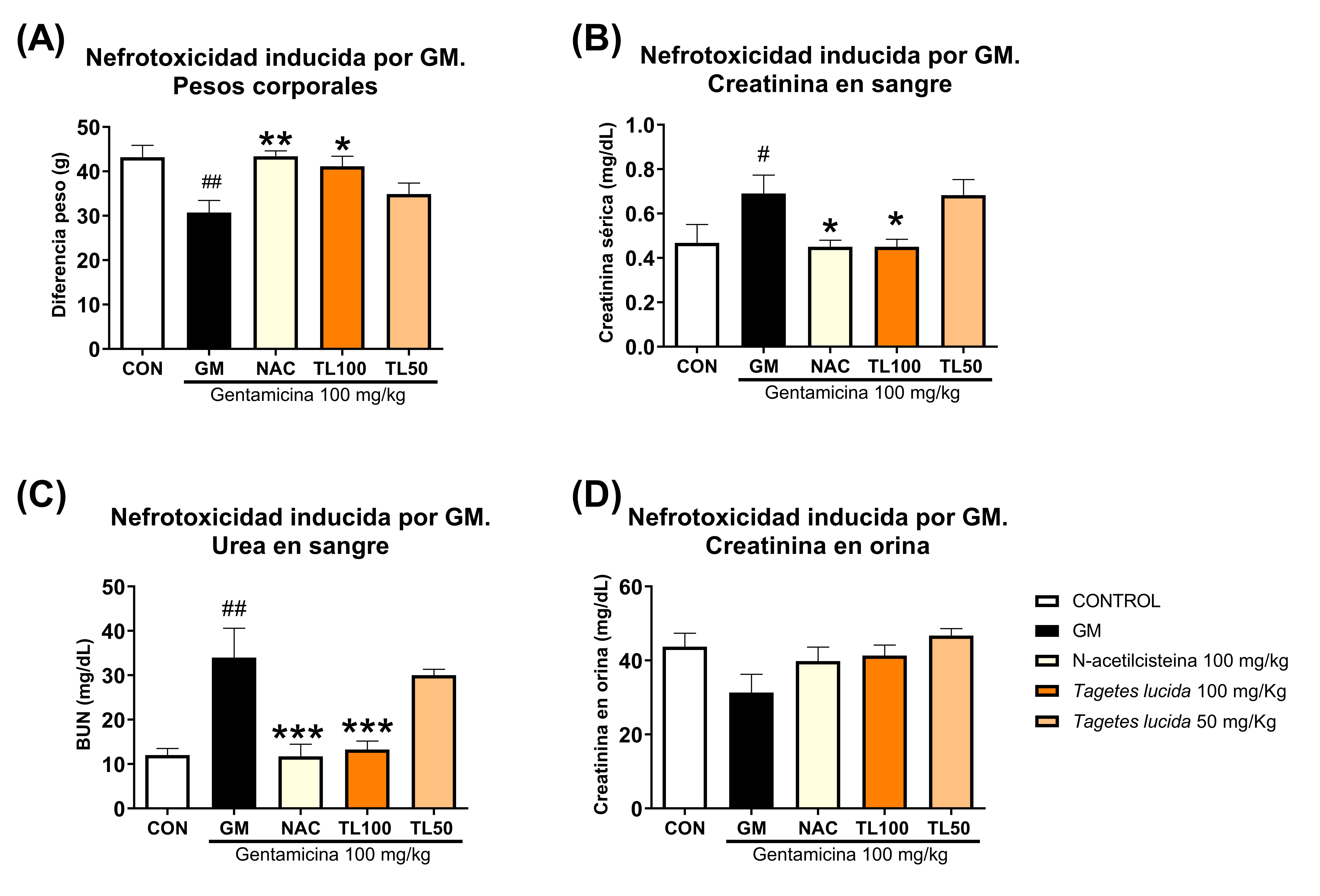
There are multiple noxious factors for the kidney that have a considerable impact on public health, such as hypertension, diabetes, exposure to nephrotoxic drugs, polluting environmental factors such as heavy metals or pesticides, and chronic dehydration, among others. Several species are traditionally used for the treatment of conditions associated with the kidney, with an important relationship with the blood purification system, substance excretion, and renal protection. However, the nephroprotective activity of species traditionally reported in Guatemala for kidney disorders has not been explored to date. This study aimed to evaluate the in vivo protective effects of an ethanolic extract of Tagetes lucida Cav. against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity, streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy, and dehydration produced by heat exposure. Nephrotoxicity was induced in male rats by the administration of intraperitoneal gentamicin (IP, 100 mg/kg) for 8 days; diabetes was induced by streptozotocin (110 mg/kg IP) with evaluation of diabetic progression for 3 months; and dehydration was produced by continuous heat exposure of 1.5 hours at 37° C for 5 weeks, assessing body weight, blood glucose, creatinine, urea and protein in blood and urine. Oral administration of 100 mg/Kg of T. lucida significantly attenuated (P ˂ 0.05) the elevation of creatinine and urea levels in rats exposed to gentamicin and in diabetic nephropathy in mice. Finally, the T. lucida extract significantly suppressed the elevation of urea levels in urine compared to the water-deprived heat-dehydrated control group. These data suggest that T. lucida has potential nephroprotective and metabolic effects that could be beneficial in preventing kidney damage.
Downloads
References
Abdel-Azeem, A. S., Hegazy, A. M., Zeidan, H. M., Ibrahim, K. S., & El-Sayed, E. M. (2017). Potential Renoprotective Effects of Rosemary and Thyme Against Gentamicin Toxicity in Rats. Journal of Dietary Supplements, 14(4), 380-394. https://doi.org/10.1080/19390211.2016.1253632
Abdel-Haleem, S. A., Ibrahim, A. Y., Ismail, R. F., Shaffie, N. M., Hendawy, S. F., & Omer, E. A. (2017). In-vivo hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic properties of Tagetes lucida alcoholic extract in streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemic Wistar albino rats. Annals of Agricultural Sciences, 62(2), 169-181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2017.11.005
Al-Shabanah, O. A., Aleisa, A. M., Al-Yahya, A. A., Al-Rejaie, S. S., Bakheet, S. A., Fatani, A. G., & Sayed-Ahmed, M. M. (2010). Increased urinary losses of carnitine and decreased intramitochondrial coenzyme A in gentamicin-induced acute renal failure in rats. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, 25(1), 69-76. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfp457
Ankli, A., Sticher, O., & Heinrich, M. (1999). Medical ethnobotany of the Yucatec Maya: Healers’ consensus as a quantitative criterion. Economic Botany, 53(2), 144-160. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02866493
Arjinajarn, P., Pongchaidecha, A., Chueakula, N., Jaikumkao, K., Chatsudthipong, V., Mahatheeranont, S., Norkaew, O., Chattipakorn, N., & Lungkaphin, A. (2016). Riceberry bran extract prevents renal dysfunction and impaired renal organic anion transporter 3 (Oat3) function by modulating the PKC/Nrf2 pathway in gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Phytomedicine, 23(14), 1753-1763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2016.10.014
Ayala Lemus, M. L. (1999). Etnobotánica con énfasis en el aspecto agronómico de las plantas medicinales usadas por el grupo étnico k’aqchikel en el municipio de Tecpán Guatemala, Chimaltenango [Tesis de licenciatura, Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala]. Centro de Documentación e Información Agrícola, Facultad de Agronomnía. http://fausac.usac.edu.gt/tesario/tesis/T-01805.pdf
Bae, E. H., Kim, I. J., Joo, S. Y., Kim, E. Y., Choi, J. S., Kim, C. S., Ma, S. K., Lee, J., & Kim, S. W. (2014). Renoprotective effects of the direct renin inhibitor aliskiren on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Journal of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System, 15(4), 348-361. https://doi.org/10.1177/1470320312474853
Barreno Ortiz, F. M. (2012). Estudio etnobotánico medicinal en 11 municipios de la Reserva de Usos Múltiples Cuenca del Lago de Atitlán, Sololá [Tesis de licenciatura, Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala]. Centro de Documentación y Biblioteca de Farmacia, Facultad de ciencias Químicas y Farmacia. https://biblioteca-farmacia.usac.edu.gt/Tesis/B238.pdf
Bream, K. D. W., Breyre, A., Garcia, K., Calgua, E., Chuc, J. M., & Taylor, L. (2018). Diabetes prevalence in rural Indigenous Guatemala: A geographic-randomized cross-sectional analysis of risk. PLoS ONE, 13(8), Artículo e0200434. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0200434
Cáceres, A., Girón, L. M., & Martínez, A. M. (1987). Diuretic activity of plants used for the treatment of urinary ailments in guatemala. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 19(3), 233-245. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-8741(87)90001-8
Castañeda, R., Cáceres, A., Cruz, S. M., Aceituno, J. A., Marroquín, E. S., Barrios Sosa, A. C., Strangman, W. K., & Williamson, R. T. (2023). Nephroprotective plant species used in traditional Mayan Medicine for renal-associated diseases. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 301, Artículo 115755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2022.115755
Castañeda, R., Cáceres, A., Velásquez, D., Rodríguez, C., Morales, D., & Castillo, A. (2022). Medicinal plants used in traditional Mayan medicine for the treatment of central nervous system disorders: An overview. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 283, Artículo 114746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2021.114746
Castañeda, R., Ortiz, E., Aldana, C., Cruz, S. M., & Cáceres, A. (2020). Biomarcadores traslacionales de modelos in vitro e in vivo de daño renal: Una perspectiva para abordar nefrotoxicidad desde múltiples factores etiológicos. Ciencia, Tecnología y Salud, 7(1), 107-128. https://doi.org/10.36829/63cts.v7i1.893
Cleaves Herrera, C. I. (2001). Etnobotánica médica participativa en siete comunidades de la zona de influencia del parque nacional laguna Lachuá, Cobán, Alta Verapaz, Guatemala [Tesis de licenciatura, Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala]. Centro de Documentación y Biblioteca de Farmacia, Facultad de ciencias Químicas y Farmacia. https://biblioteca-farmacia.usac.edu.gt/Tesis/B120.pdf
Deshpande, A. D., Harris-Hayes, M., & Schootman, M. (2008). Epidemiology of diabetes and diabetes-related complications. Physical Therapy, 88(11), 1254-1264. https://doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20080020
El-Kashef, D. H., El-Kenawi, A. E., Suddek, G. M., & Salem, H. A. (2015). Flavocoxid attenuates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Archives of Pharmacology, 388(12), 1305-1315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1164-8
Estrada-Soto, S., González-Trujano, M. E., Rendón-Vallejo, P., Arias-Durán, L., Ávila-Villarreal, G., & Villalobos-Molina, R. (2021). Antihypertensive and vasorelaxant mode of action of the ethanol-soluble extract from
Tagetes lucida Cav. aerial parts and its main bioactive metabolites. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 266, Artículo 113399 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2020.113399
García-Arroyo, F. E., Gonzaga, G., Muñoz-Jiménez, I., Osorio-Alonso, H., Iroz, A., Vecchio, M., Tapia, E., Roncal-Jimenez, C. A., Johnson, R. J., & Sánchez-Lozada, L. G. (2019). Antioxidant supplements as a novel mean for blocking recurrent heat stress-induced kidney damage following rehydration with fructose-containing beverages. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 141, 182-191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.06.016
García-Arroyo, F. E., Tapia, E., Blas-Marron, M. G., Gonzaga, G., Silverio, O., Cristóbal, M., Osorio, H., Arellano-Buendía, A. S., Zazueta, C., Aparicio-Trejo, O. E., Reyes-García, J. G., Pedraza-Chaverri, J., Soto, V., Roncal-Jimenez, C., Johnson, R. J., & Sánchez-Lozada, L. G. (2017). Vasopressin mediates the renal damage induced by limited fructose rehydration in recurrently dehydrated rats. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 13(8), 961-975. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.20074
Garud, M. S., & Kulkarni, Y. A. (2017). Attenuation of renal damage in type I diabetic rats by umbelliferone – a coumarin derivative. Pharmacological Reports, 69(6), 1263-1269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2017.06.014
Giovannini, P., Howes, M. J. R., & Edwards, S. E. (2016). Medicinal plants used in the traditional management of diabetes and its sequelae in Central America: A review. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 184, 58-71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2016.02.034
Girón, L. M., Freire, V., Alonzo, A., & Cáceres, A. (1991). Ethnobotanical survey of the medicinal flora used by the Caribs of Guatemala. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 34(2-3), 173-187. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-8741(91)90035-C
Guadarrama-Cruz, G., Alarcon-Aguilar, F. J., Lezama-Velasco, R., Vazquez-Palacios, G., & Bonilla-Jaime, H. (2008). Antidepressant-like effects of Tagetes lucida Cav. in the forced swimming test. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 120(2), 277-281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2008.08.013
Guadarrama-Cruz, G., Alarcón-Aguilar Francisco, J., Vega-Avila, E., Vázquez-Palacios, G., & Bonilla-Jaime, H. (2012). Antidepressant-like effect of Tagetes lucida Cav. extract in rats: Involvement of the serotonergic system. American Journal of Chinese Medicine, 40(4), 753-768. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X12500565
Guo, X., Meng, Q., Liu, Q., Wang, C., Sun, H., Peng, J., Ma, X., Kaku, T., & Liu, K. (2013). JBP485 improves gentamicin-induced acute renal failure by regulating the expression and function of Oat1 and Oat3 in rats. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 271(2), 285-295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2013.04.029
Hassanein, E. H. M., Ali, F. E. M., Kozman, M. R., & Abd El-Ghafar, O. A. M. (2021). Umbelliferone attenuates gentamicin-induced renal toxicity by suppression of TLR-4/NF-κB-p65/NLRP-3 and JAK1/STAT-3 signaling pathways. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(9), 11558-11571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11416-5
Hernandez-Leon, A., González-Trujano, M. E., Narváez-González, F., Pérez-Ortega, G., Rivero-Cruz, F., & Aguilar, M. I. (2020). Role of β-caryophyllene in the antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of Tagetes lucida Cav. Essential oil. Molecules, 25(3), Artículo 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030675
Hitziger, M. (2016). Mayan phytotherapy in Guatemala: A transdisciplinary study for ethnographic documentation and local empowerment [Tesis de doctorado, ETH Zürich]. Repository for Publications and Research Data. ETH Zurich Research Collection. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-010735971
Hitziger, M., Heinrich, M., Edwards, P., Pöll, E., Lopez, M., & Krütli, P. (2016). Maya phytomedicine in Guatemala - Can cooperative research change ethnopharmacological paradigms? Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 186, 61-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2016.03.040
Horváth, B., Mukhopadhyay, P., Kechrid, M., Patel, V., Tanchian, G., Wink, D. A., Gertsch, J., & Pacher, P. (2012). Β-Caryophyllene ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in a cannabinoid 2 receptor-dependent manner. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 52(8), 1325-1333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.01.014
Kufer, J., Heinrich, M., Förther, H., & Pöll, E. (2010). Historical and modern medicinal plant uses — the example of the Ch’orti‘ Maya and Ladinos in Eastern Guatemala. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 57(9), 1127-1152. https://doi.org/10.1211/jpp.57.9.0008
Laux, T. S., Barnoya, J., Cipriano, E., Herrera, E., Lopez, N., Polo, V. S., & Rothstein, M. (2016). Prevalence of chronic kidney disease of non-Traditional causes in patients on hemodialysis in southwest Guatemala. Revista Panamericana de Salud Publica/Pan American Journal of Public Health, 39(4), 186-193.
Luyckx, V. A., Tonelli, M., & Stanifer, J. W. (2018). The global burden of kidney disease and the sustainable development goals. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 96(6), 414-422C. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.17.206441
Mahmoud, Y. I. (2017). Kiwi fruit (Actinidia deliciosa) ameliorates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in albino mice via the activation of Nrf2 and the inhibition of NF-κB (Kiwi & gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity). Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy, 94, 206-218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.079
Mazzon, E., Britti, D., De Sarro, A., Caputi, A. P., & Cuzzocrea, S. (2001). Effect of N-acetylcysteine on gentamicin-mediated nephropathy in rats. European Journal of Pharmacology, 424(1), 75-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-2999(01)01130-X
Milagres, T., García-Arroyo, F. E., Lanaspa, M. A., Garcia, G., Ishimoto, T., Andres-Hernando, A., Kuwabara, M., Jensen, T., Sato, Y., Glaser, J., Sánchez-Lozada, L. G., Johnson, R. J., & Roncal-Jimenez, C. (2018). Rehydration with fructose worsens dehydration-induced renal damage. BMC Nephrology, 19, Artículo 180. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-018-0963-9
Naowaboot, J., Somparn, N., & Saenthaweesuk, S. (2020). Renoprotective effect of umbelliferone in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 10(1), 11-17. https://doi.org/10.4103/2221-1691.273089
Nayeli, M. B., Maribel, H. R., Enrique, J. F., Rafael, B. P., Margarita, A. F., Macrina, F. M., Ivan, M. D., & Manasés, G. C. (2020). Anti-inflammatory activity of coumarins isolated from Tagetes lucida Cav. Natural Product Research, 34(22), 3244-3248. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1553172
Nugent, R. A., Fathima, S. F., Feigl, A. B., & Chyung, D. (2011). The burden of chronic kidney disease on developing nations: A 21st century challenge in global health. Nephron - Clinical Practice, 118(3), c269–c277. https://doi.org/10.1159/000321382
Pardo Villegas, P. D., Burgos Barrios, C. L., & Cruz de León, H. W. (2011). Plantas medicinales y comestibles de la reserva natural de usos múltiples Monterrico –RNUMM, Taxisco, Santa Rosa (Inf-2011-24). Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala, Dirección General de Investigación, Programa Universitario de Investigación en Recursos Naturales y Ambiente, Centro de Estudios Conservacionistas y Centro de Datos para la Conservación
Pérez-Ortega, G., González-Trujano, M. E., Ángeles-López, G. E., Brindis, F., Vibrans, H., & Reyes-Chilpa, R. (2016). Tagetes lucida Cav.: Ethnobotany, phytochemistry and pharmacology of its tranquilizing properties. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 181, 221-228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2016.01.040
Pickersgill, B. (2016). Domestication of plants in Mesoamerica: An archaeological review with some ethnobotanical interpretations. En R. Lira, A. Casas & J. Blancas (Eds.), Ethnobotany of Mexico, Interactions of people and plants in mesoamerica (pp. 207-231). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6669-7_9
Romero, F., Pérez, M., Chávez, M., Parra, G., & Durante, P. (2009). Effect of uric acid on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats - Role of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology, 105(6), 416-424. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2009.00466.x
Roncal Jimenez, C. A., Ishimoto, T., Lakknaspa, M. A., Rivard, C. J., Nakagawa, T., Ejaz, A. A., Cicerchi, C., Inaba, S., Le, M., Miyazaki, M., Glaser, J., Correa-Rotter, R., González, M. A., Aragón, A., Wesseling, C., Sánchez-Lozada, L. G., & Johnson, R. J. (2014). Fructokinase activity mediates dehydration-induced renal injury. Kidney International, 86(2), 294-302. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2013.492
Roncal-Jimenez, C. A., Milagres, T., Andres-Hernando, A., Kuwabara, M., Jensen, T., Song, Z., Bjornstad, P., Garcia, G. E., Sato, Y., Sanchez-Lozada, L. G., Lanaspa, M. A., & Johnson, R. J. (2017). Effects of exogenous desmopressin on a model of heat stress nephropathy in mice. American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology, 312(3), F418-F426. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00495.2016
Sánchez-Lozada, L.-G., García-Arroyo, F. E., Gonzaga, G., Silverio, O., Blas-Marron, M. G., Muñoz-Jimenez, I., Tapia, E., Osorio-Alonso, H., Madero, M., Roncal-Jiménez, C. A., Weiss, I., Glaser, J., & Johnson, R. J. (2018). Kidney injury from recurrent heat stress and rhabdomyolysis: Protective role of allopurinol and sodium bicarbonate. American Journal of Nephrology, 48(5), 339-348. https://doi.org/10.1159/000494663
Sandoval, M. A. (1999). Etnobotánica de las plantas medicinales usadas por la cultura K’aqchikel en el departamento de Guatemala. Informe final del proyecto No. 32/97. Secretaria Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología -Senacyt.
Sun, H., Yang, H., Ruan, H., Li, W., He, X., Wang, L., Liu, F., & Zhang, J. (2018). The protective effect of sika deer antler protein on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in Vitro and in Vivo. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 50(3), 841-850. https://doi.org/10.1159/000494471
Szkudelski, T. (2001). The mechanism of alloxan and streptozotocin action in B cells of the rat pancreas. Physiological Research, 50(6), 537-546.
Tesch, G. H., & Allen, T. J. (2007). Rodent models of streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy (methods in renal research). Nephrology, 12(3), 261-266. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1797.2007.00796.x
Tún López, F. (2017). Beneficios del uso de la medicina tradicional en la salud de las personas de la aldea La Unión cuarto pueblo, Ixcán, Quiché, Guatemala, C.A. [Tesis de maestría inédita, Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala].
Vargas, J. M. (2019). Etnofarmacología de las principales plantas medicinales utilizadas por los Q’eqchi’es en tres comunidades de Alta Verapaz, Guatemala [Tesis de doctorado, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México]. https://biblioteca-farmacia.usac.edu.gt/Tesis/TD002.pdf
Vargas, J. M., & Andrade-Cetto, A. (2018). Ethnopharmacological field study of three Q’eqchi communities in Guatemala. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9, Article 1246. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01246
Ventura-Martinez, R., Angeles-Lopez, G. E., Gonzalez-Trujano, M. E., Carrasco, O. F., & Deciga-Campos, M. (2020). Study of antispasmodic and antidiarrheal activities of Tagetes lucida (mexican tarragon) in experimental models and its mechanism of action. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2020, Article ID 7140642,. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7140642
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Rodrigo Castañeda, Caroline Aldana, Agustín Aceituno, David Morales, Diana Velasquez, Cesar Rodriguez, Sully Cruz

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
El autor que publique en esta revista acepta las siguientes condiciones:
- El autor otorga a la Dirección General de Investigación el derecho de editar, reproducir, publicar y difundir el manuscrito en forma impresa o electrónica en la revista Ciencia, Tecnología y Salud.
- La Direción General de Investigación otorgará a la obra una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0 Internacional
Funding data
-
Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala
Grant numbers B9-2020;Des3-2021









