Efecto del copolímero en bloque sulfonado sobre las propiedades térmicas y de equilibrio de una membrana sulfonada mezclada con un fluoropolímero en bloque
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36829/63CTS.v8i1.887Resumen
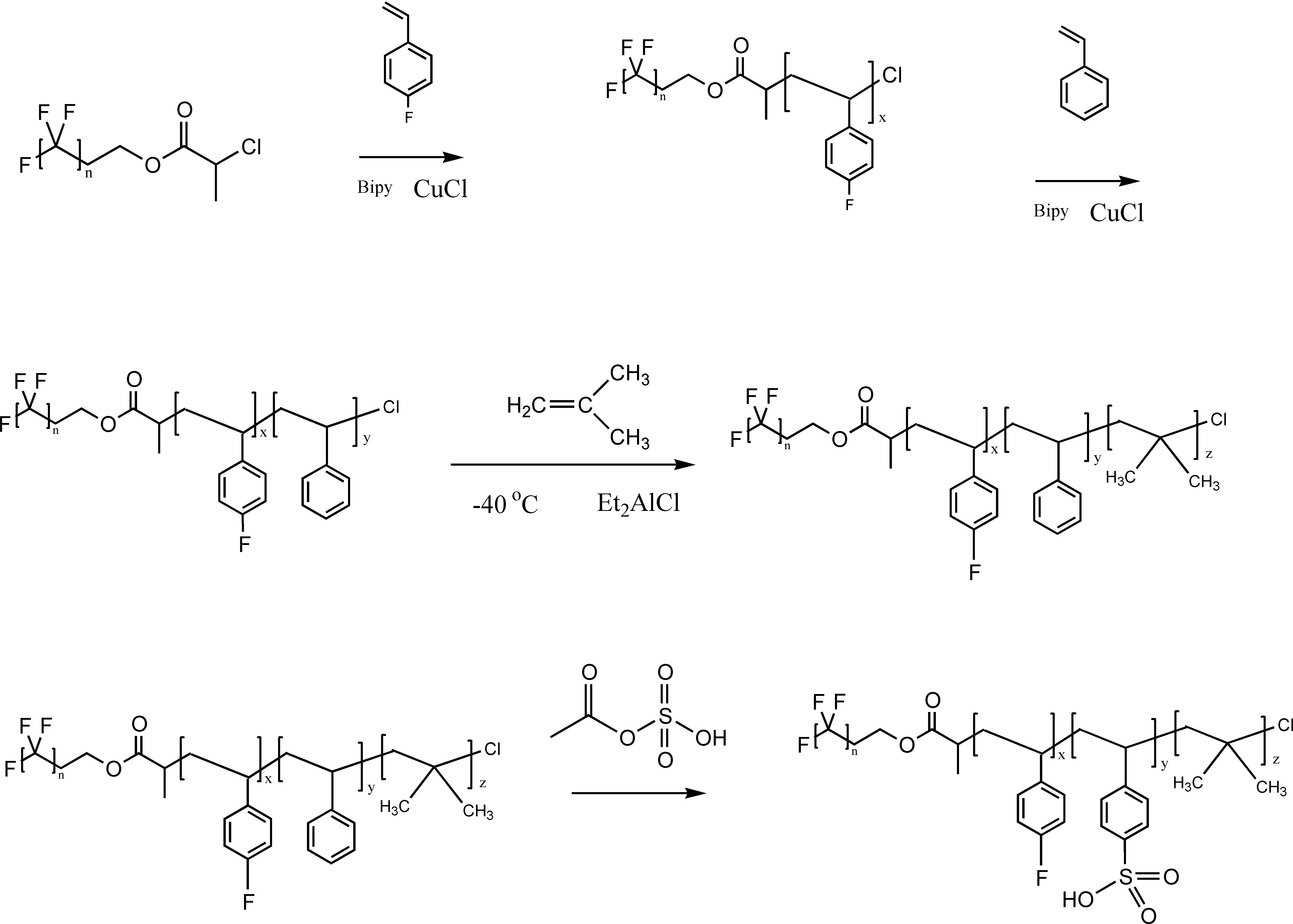
La tecnología de membranas poliméricas requiere de la síntesis de nuevos polímeros que mejoren sus propiedades de equilibrio, térmicas y de transporte. Esta investigación tuvo como objetivo determinar las propiedades de equilibrio y térmicas de una membrana compuesta de poli(estireno isobutileno estireno) sulfonado (SIBS SO3H) y un fluoropolímero en bloque sulfonado compuesto de poli(4-fluorostireno) (P4FS), poli(estireno) (PS) y poli(isobutileno) (PIB). El fluoropolímero en bloque se sintetizó utilizando la técnica de polimerización radical por transferencia atómica (ATRP por sus siglas en inglés) y polimerización catiónica. El peso molecular y la estabilidad térmica del fluoropolímero en bloque fueron determinadas por medio de Cromatografía de Permeación en Gel (GPC) y un análisis termogravimétrico (TGA). La composición química se monitorizó utilizando espectroscopía infrarroja por transformada de Fourier (FTIR) y espectroscopía de Resonancia Magnética Nuclear (RMN). El peso molecular de P4FS-b-PS fue Mn ~ 36,100; este valor aumentó un 8% después de la polimerización catiónica. Las propiedades de equilibrio de la membrana fueron evaluadas por medio de la absorción de agua y la capacidad de intercambio iónico. El comportamiento de degradación y las transiciones térmicas se determinaron utilizando TGA y Calorimetría Diferencial de Barrido (DSC). Esta nueva membrana exhibió una absorción de agua mayor del 608% relacionada con la mejora del 36% en la capacidad de intercambio iónico y el incremento en 25.31% y 25.24% en la energía requerida para producir las transiciones termales inducidas por la adición del fluoropolímero sulfonado en bloque.
Descargas
Citas
Ahmad, S., & Ahmed, S. K. M. (2014). Application of membrane technology in food processing. In A. Malik, Z. Erginkaya, S. Ahmad & H. Erten (Eds.), Food Processing: Strategies for Quality Assessment (pp. 379-394). Springer New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-1378-7_15
Alaswad, A., Palumbo, A., Dassisti, M., & Olabi, A. G. (2016). Fuel cell technologies, applications, and state of the art. A reference guide. In Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-803581-8.04009-1
Avilés-Barreto, S. L., & Suleiman, D. (2013). Transport properties of sulfonated poly (styrene- isobutylene-styrene) membranes with counter-ion substitution. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 129(4), 2294-2304. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.38952
Barreto, S. M. A., & Suleiman, D. (2010). Synthesis and characterization of sulfonated poly(styrene- isoprene-styrene): Effects of linear vs. branched morphology and counter-ion substitution. Journal of Membrane Science, 362(1-2), 471-477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2010.06.061
Elabd, Y. A., & Hickner, M. A. (2011). Block copolymers for fuel cells. Macromolecules, 44(1), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma101247c
Elabd, Y. A., Napadensky, E., Sloan, J. M., Crawford, D. M., & Walker, C. W. (2003). Triblock copolymer ionomer membranes: Part I. Methanol and proton transport. Journal of Membrane Science, 217(1-2), 227-242. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(03)00127-3
Elabd, Y. A., Napadensky, E., Walker, C. W., & Winey, K. I. (2006). Transport properties of sulfonated poly(styrene-b-isobutylene-b-styrene) triblock copolymers at high ion-exchange capacities. Macromolecules, 39(1), 399-407. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma051958n
Guerrero-Gutiérrez, E. M. A., Pérez-Pérez, M., Newbloom, G. M., Pozzo, L. D., & Suleiman, D. (2017). Effect of block composition on the morphology and transport properties of sulfonated f luoroblock copolymer blend membranes. Polymer Engineering and Science, 57(11), 1262-1272. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.24508
Guerrero- Gutiérrez, E. M. A., Pérez-Pérez, M., & Suleiman, D. (2015). Synthesis and characterization of sulfonated fluorinated block copolymer membranes with different esterified initiators for DMFC applications. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 132(23). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.42046
Huang, Q., Cheng, Y., Zhang, S., Liu, H., & Liao, H. (2019). Blend proton exchange membranes with high performance based on sulfonated poly(arylene ether phosphine oxide)s and poly(vinylidene fluoride). Journal of Materials Science, 54(6), 5176-5186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-03202-z
Jankova, K., & Hvilsted, S. (2003). Preparation of Poly(2,3,4,5,6-pentaf luorostyrene) and block copolymers with styrene by ATRP. Macromolecules, 36(5), 1753-1758. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma021039m
Jankova, K., & Hvilsted, S. (2005). Novel fluorinated block copolymer architectures fuelled by atom transfer radical polymerization. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 126(2), 241-250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluchem.2004.11.002
Jung, B., Kim, B., & Yang, J. M. (2004). Transport of methanol and protons through partially sulfonated polymer blend membranes for direct methanol fuel cell. Journal of Membrane Science, 245(1-2), 61-69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2004.07.016
Kraytsberg, A., & Ein-Eli, Y. (2014). Review of advanced materials for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Energy & Fuels, 28(12), 7303-7330. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef501977k
Kumari, M., Sodaye, H. S., Sen, D., & Bindal, R. C. (2018). Properties and morphology studies of proton exchange membranes based on cross-linked sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) for electrochemical application: Effect of cross- linker chain length. Solid State Ionics, 316, 75-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2017.12.027
Kusoglu, A., Vezzù, K., Hegde, G. A., Nawn, G., Motz, A. R., Sarode, H. N., Haugen, G. M., Yang, Y., Seifert, S., Yandrasits, M. A., Hamrock, S., Maupin, C. M., Weber, A. Z., Di Noto, V., &rring, A. M. (2020). Transport and morphology of a proton exchange membrane based on a doubly functionalized perfluorosulfonic imide side chain perflourinated polymer. Chemistry of Materials, 32(1), 38-59. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b05012
Kusoglu, A., & Weber, A. Z. (2017). New insights into perfluorinated sulfonic-acid ionomers. Chemical Reviews, 117(3), 987-1104. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00159
Madaeni, S. S., Ghaemi, N., & Rajabi, H. (2015). Advances in polymeric membranes for water treatment. In A. Basile, A. Cassano, & N. K. Rastogi (Eds.), Advances in Membrane Technologies for Water Treatment (Part One, pp. 3-41). Woodhead Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-78242-121-4.00001-0
Mauritz, K. A., & Moore, R. B. (2004). State of understanding of Nafion. Chemical Reviews, 104(10), 4535-4586. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr0207123
Matyjaszewski, K. (2012). Atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP): Current status and future perspectives. Macromolecules, 45(10), 4015-4039. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma3001719
Ortiz-Negrón, A., & Suleiman, D. (2015). The effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on the properties of sulfonated block copolymers. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 132(41), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.42651
Peighambardoust, S. J., Rowshanzamir, S., & Amjadi, M. (2010). Review of the proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 35(17), 9349-9384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.05.017
Pérez-Pérez, M., & Suleiman, D. (2015). Transport properties of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) membranes with counter-ion substitution. Journal of Membrane Science, 493, 414-427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2015.06.017
Pérez-Pérez, M., & Suleiman, D. (2016). Effect of block composition on the morphology, hydration, and transport properties of sulfonated PS-b- PEGPEM-b-PS. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 133(48), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.44343
Perrier, S., Jackson, S. G., Haddleton, D. M., & Ameduri, B. (2002). Preparation of fluorinated methacrylic copolymers by copper mediated living radical polymerization. Tetrahedron, 58, 4053-4059. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4020(02)00274-0
Rosen, S. (1993). Fundamental Principles of Polymeric Materials (2nd). Wiley Interscience Publication.
Ruiz-Colón, E., Pérez-Pérez, M., & Suleiman, D. (2018). Influence of carboxylated and phosphonated single-walled carbon nanotubes on the transport properties of sulfonated poly(styrene-isobutylene- styrene) membranes. Journal of Polymer Science, Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 56(21), 2475-2495. https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.29222
Santoro, C., Arbizzani, C., Erable, B., & Ieropoulos, I. (2017). Microbial fuel cells: From fundamentals to applications. A review. Journal of Power Sources, 356, 225-244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.03.109
Seleem, S., Hopkins, M., Olivio, J., & Schiraldi, D. A. (2017). Comparison of thermal decomposition of polystyrene products vs. bio-based polymer aerogels. Ohio Journal of Science, 117(2), 50-60. https://doi.org/10.18061/ojs.v117i2.5828
Suleiman, D., Napadensky, E., Sloan, J. M., & Crawford, D. M. (2007). Thermogravimetric characterization of highly sulfonated poly(styrene-isobutylene- styrene) block copolymers: Effects of sulfonation and counter- ion substitution. Thermochimica Acta, 460(1-2), 35-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2005.01.030
Shimura, T., Miyatake, K., & Watanabe, M. (2008). Poly(arylene ether) ionomers containing sulfofluorenyl groups: Effect of electron- withdrawing groups on the properties. European Polymer Journal, 44(12), 4054- 4062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2008.09.017
Singh, R. (2015). Chapter 1-Introduction to Membrane Technology. In R. Singh (Ed.), Membrane Technology and Engineering for Water Purification (2nd, pp. 1-80). Butterworth- Heinemann. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63362-0.00001-X
Toman, L., Janata, M., Spěváček, J., Vlček, P., Látalová, P., Sikora, A., & Masař, B. (2005). Synthesis of methyl methacrylate, styrene, and isobutylene multiblock copolymers using atom transfer and cationic polymerization. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 43(17), 3823- 3830. https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.20884
Xie, H., Tao, D., Xiang, X., Ou, Y., Bai, X., & Wang, L. (2015). Synthesis and properties of highly branched star-shaped sulfonated block poly(arylene ether)s as proton exchange membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 473(0), 226 -236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.09.015
Ye, H., Li, D., Ye, X., Zheng, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhang, H., & Chen, Z. (2019). An adjustable permeation membrane up to the separation for multicomponent gas mixture. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-43751-0
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2021 Edward M. A. Guerrero-Gutiérrez

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.
El autor que publique en esta revista acepta las siguientes condiciones:
- El autor otorga a la Dirección General de Investigación el derecho de editar, reproducir, publicar y difundir el manuscrito en forma impresa o electrónica en la revista Ciencia, Tecnología y Salud.
- La Direción General de Investigación otorgará a la obra una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0 Internacional









