Phosphorus solubilization efficiency of native Guatemalan isolates of Pseudomonas fluorescens
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36829/63CTS.v8i2.923Keywords:
Phosphorus solubilization, Andisols, genetic diversity, solubilization index, solubilization stabilityAbstract
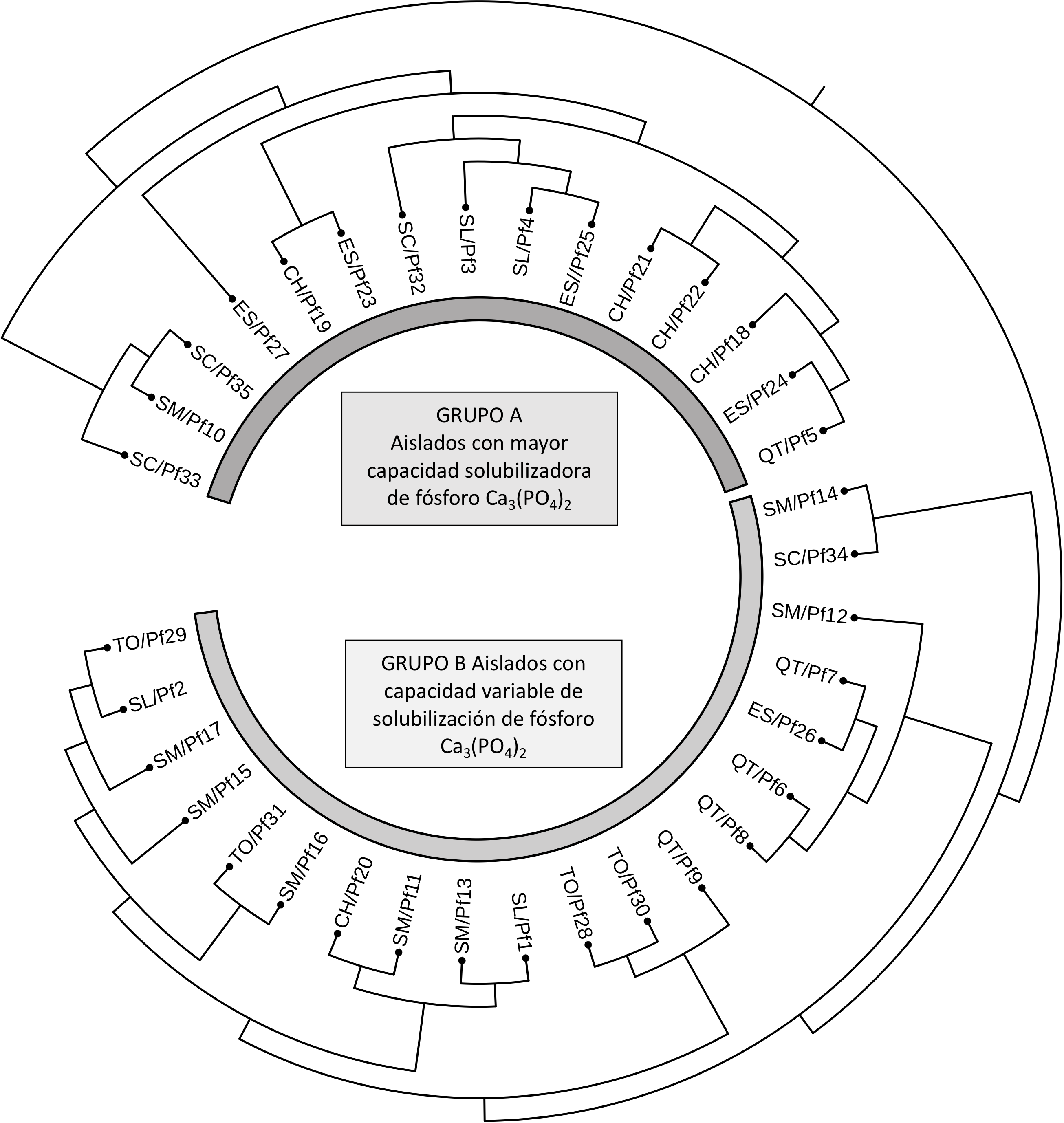
Phosphorus (P) is an essential element in agricultural production, but due to its complex dynamics in the soil, only a tiny amount is usable by plants. This is because most P is in insoluble forms, especially in volcanic Andisol soils. Microorganisms with phosphorus solubilizing capacity (MSF) are an alternative for transforming P into soluble forms usable by plants and providing multiple environmental benefits. This research identified and evaluated in vitro native isolates of Pseudomonas fluorescens Mingula, obtained from Guatemalan regions with Andisol soils that limit agricultural production due to high P fixation. In vitro cultures of the bacteria were grown on the National Botanical Research Institute's phosphate medium (NBRIP), with tricalcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2 as a source of insoluble P, and We measured the phosphorus solubilization index (PSI). We identified and confirmed a total of 35 isolates of P. fluorescens by specific PCR. Using the AFLP marker, genetic relationship analysis showed two groups: group A included isolates with PSI greater than 1.75, while group B included those with FSI less than 1.75. Comparing of PSI between isolates and departments showed statistically significant differences (p < .001), respectively, with the Pf_33 isolate as the most efficient. Because of the high solubilization potential of the native isolates of genetic group A (FSI > 1.75), We recommend future research to determine their response to field conditions and strategies for biofertilizer development.
Downloads
References
Abdul-Wahab, A., Taj-Aldeen, S. J., Hagen, F., Diophode, S., Saadoon, A., Meis, J. F., & Klaassen, C. H. (2014). Genotypic diversity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis siblings in Qatar using AFLP fingerprinting. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 33(2), 265-271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-013-1954-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-013-1954-1
AL-Ani, M. A. M., Hmoshi, R. M., Kanaan, I. A., & Thanoon, A. A. (2019). Effect of pesticides on soil microorganisms. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1294(7). Artículo 072007. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1294/7/072007 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1294/7/072007
AlKhader, A. M. (2015). The impact of phosphorus fertilizers on heavy metals content of soils and vegetables grown on selected farms in jordan. Agrotechnology, 5(1), Artículo 1000137. https://doi.org/10.4172/2168-9881.1000137 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4172/2168-9881.1000137
Alori, E. T., Glick, B. R., & Babalola, O. O. (2017). Microbial phosphorus solubilization and its potential for use in sustainable agriculture. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00971 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00971
Arora, S., & Sahni, D. (2016). Pesticides effect on soil microbial ecology and enzyme activity- An overview. Journal of Applied and Natural Science, 8(2), 1126-1132. https://doi.org/10.31018/jans.v8i2.929 DOI: https://doi.org/10.31018/jans.v8i2.929
Azziz, G., Bajsa, N., Haghjou, T., Taulé, C., Valverde, A., Igual, J. M., & Arias, A. (2012). Abundance, diversity and prospecting of culturable phosphate solubilizing bacteria on soils under crop–pasture rotations in a no-tillage regime in Uruguay. Applied Soil Ecology, 61, 320-326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2011.10.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2011.10.004
Batool, S., & Iqbal, A. (2019). Phosphate solubilizing rhizobacteria as alternative of chemical fertilizer for growth and yield of Triticum aestivum (Var. Galaxy 2013). Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 26(7), 1400-1410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.05.024 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.05.024
Becerra, J. M., Quintero, D., Martínez, M., & Matiz, A. (2012). Caracterización de microorganismos solubilizadores de fosfato aislados de suelos destinados al cultivo de uchuva (Physalis peruviana L.). Revista Colombiana de Ciencias Hortícolas, 5(2), 186-194. https://doi.org/10.17584/rcch.2011v5i2.1265 DOI: https://doi.org/10.17584/rcch.2011v5i2.1265
Billah, M., Khan, M., Bano, A., Hassan, T. U., Munir, A., & Gurmani, A. R. (2019). Phosphorus and phosphate solubilizing bacteria: Keys for sustainable agriculture. Geomicrobiology Journal, 36(10), 904-916. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2019.1654043 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2019.1654043
Borie, F., & Rubio, R. (2003). Total and organic phosphorus in Chilean volcanic soils. Gayana Botanica, 60, 69-78. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-66432003000100011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-66432003000100011
Breitkreuz, C., Buscot, F., Tarkka, M., & Reitz, T. (2020). Shifts between and among population of wheat rhizosphere Pseudomonas, Streptomyces and Phyllobacterium suggest consistent phosphate mobilization at different wheat growth stages under abiotic stress. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 3109. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.03109 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.03109
Browne, P., Rice, O., Miller, S. H., Burke, J., Dowling, D. N., Morrissey, J. P., & O’Gara, F. (2009). Superior inorganic phosphate solubilization is linked to phylogeny within the Pseudomonas fluorescens complex. Applied Soil Ecology, 43(1), 131-138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2009.06.010 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2009.06.010
Callejas-Cañarte, G. V., Cisneros-Rojas, C. A., & Caicedo-Bejarano, L. D. (2018). Capacidad solubilizadora de fosfato de aluminio por hongos rizosféricos aislados de un Andisol colombiano. Entramado, 14(2), 218-227. https://doi.org/10.18041/1900-3803/entramado.2.4745 DOI: https://doi.org/10.18041/1900-3803/entramado.2.4745
Cerón, L., & Aristizábal, F. (2012). Dinámica del ciclo del nitrógeno y fósforo en suelos. Revista Colombiana de Biotecnología, 14(1), 285-295.
Chan-Cupul, W., Juárez-González, M., Ruiz-Sánchez, E., Sánchez-Rangel, J., Molina-Ochoa, J., & Galindo-Velasco, E. (2018). Solubilización de fuentes inorgánicas de fósforo por micromicetos aislados de la rizósfera de papaya var. Maradol (Carica papaya L.) y su susceptibilidad a herbicidas convencionales. Revista Internacional de Contaminacion Ambiental, 34(2), 281-284. https://doi.org/10.20937/rica.2018.34.02.09 DOI: https://doi.org/10.20937/RICA.2018.34.02.09
Chawngthu, L., Hnamte, R., & Lalfakzuala, R. (2020). Isolation and characterization of rhizospheric phosphate solubilizing bacteria from wetland paddy field of Mizoram, India. Geomicrobiology Journal, 37(4), 366-375. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2019.1709108 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2019.1709108
Chowdhury, R. B., Moore, G. A., Weatherley, A. J., & Arora, M. (2017). Key sustainability challenges for the global phosphorus resource, their implications for global food security, and options for mitigation. Journal of Cleaner Production, 140, 945-963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.07.012 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.07.012
Cordell, D., Drangert, J. O., & White, S. (2009). The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Global Environmental Change, 19(2), 292-305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2008.10.009 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2008.10.009
Cordell, D., Rosemarin, A., Schröder, J. J., & Smit, A. L. (2011). Towards global phosphorus security: a systems framework for phosphorus recovery an reuse options. Chemosphere, 84(6), 747–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.02.032 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.02.032
Corrales-Ramírez, L. C., Arévalo-Galvez, Z. Y., & Moreno-Burbano, V. E. (2014). Solubilización de fosfatos: una función microbiana importante en el desarrollo vegetal. NOVA Publicación Científica en Ciencias Biomédicas, 12(21), 67-79. https://doi.org/10.22490/24629448.997 DOI: https://doi.org/10.22490/24629448.997
Dahlgren, R. A., Saigusa, M., & Ugolini, F. (2004). The nature, properties and management of volcanic soils. Advanced Agronomy, 82, 113-181. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2113(03)82003-5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2113(03)82003-5
de Mendiburu, F. & Yassen, M. (2020). agricolae: Statistical procedures for agricultural research. R package version 1.4.0. https://myaseen208.github.io/agricolae/https://cran.r-project.org/package=agricolae.
Delfim, J., Schoebitz, M., Paulino, L., Hirzel, J., & Zagal, E. (2018). Phosphorus availability in wheat, in volcanic soils inoculated with phosphate-solubilizing Bacillus thuringiensis. Sustainability, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010144 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010144
Delgado-Baquerizo, M., Grinyer, J., Reich, P. B., & Singh, B. K. (2016). Relative importance of soil properties and microbial community for soil functionality: Insights from a microbial swap experiment. Functional Ecology, 30(11), 1862-1873. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12674 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12674
Dijkstra, P., Thomas, S. C., Heinrich, P. L., Koch, G. W., Schwartz, E., & Hungate, B. A. (2011). Effect of temperature on metabolic activity of intact microbial communities: Evidence for altered metabolic pathway activity but not for increased maintenance respiration and reduced carbon use efficiency. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 43(10), 2023-2031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.05.018 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.05.018
Elekhtyar, N. (2016). Efficiency of Pseudomonas fluorescens as plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) for the enhancement of seedling vigor, nitrogen uptake, yield and its atrributes of rice (Oryza sativa L.). International Journal of Scientific Research in Agricultural Sciences, 2, 57-67.
Espinosa-Sánchez, J. A., & Sanabria, Y. R. (2015). Procesos específicos de formación en Andisoles, Alfisoles y Ultisoles en Colombia. Escuela de Ingeniería de Antioquia, 12(3), E85-E97. https://doi.org/10.14508/reia.2015.11.E2.85-97
Francioli, D., Schulz, E., Lentendu, G., Wubet, T., Buscot, F., & Reitz, T. (2016). Mineral vs. organic amendments: Microbial community structure, activity and abundance of agriculturally relevant microbes are driven by long-term fertilization strategies. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7, Artículo 1446. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01446. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01446
Gayosso-Barragán, O., Rodríguez-Herrera, S. A., López-Benítez, A., & Luevanos-Escareño, M. P. (2017). Aislamiento e identificación de bacterias solubilizadoras de fosfatos y su potencial para disolver fosfato tricálcico. Revista de Investigación y Desarrollo, 3(7), 33-37.
Goteti, P. K., Desai, S., Emmanuel, L. D. A., Taduri, M., & Sultana, U. (2014). Phosphate solubilization potential of fluorescent Pseudomonas spp. isolated from diverse agro-ecosystems of india. International Journal of Soil Science, 9(3), 101-110. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijss.2014.101.110 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3923/ijss.2014.101.110
Hariprasad, P., & Niranjana, S. (2009). Isolation and characterization of phosphate solubilizing rhizobacteria to improve plant health of tomato. Plant and Soil, 316, 13-24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9754-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9754-6
Hassan, M. K., McInroy, J. A., & Kloepper, J. W. (2019). The interactions of rhizodeposits with plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in the rhizosphere: A review. Agriculture, 9(7), Artículo 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture9070142 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture9070142
Hii, Y. S., Yen San, C., Lau, S. W., & Danquah, M. K. (2020). Isolation and characterisation of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms from peat. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 26(5), Artículo 101643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101643 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101643
Hou, E., Lu, X., Jiang, L., Wen, D., & Luo, Y. (2019). Quantifying soil phosphorus dynamics: A data assimilation approach. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 124(7), 2159-2173. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JG004903 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JG004903
Islam, M. K., Sano, A., Majumder, M. S. I., Hossan, M. A., & Sakagami, J. I. (2019). Isolation and molecular characterization of phosphate solubilizing filamentous fungi from subtropical soils in Okinawa. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 17(4), 9621-9650. https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1704 DOI: https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1704_91459157
Johnsen, K., & Nielsen, P. (1999). Diversity of Pseudomonas strains isolated with King’s B and Gould’s S1 agar determined by repetitive extragenic palindromic-polymerase chain reaction, 16S rDNA sequencing and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy characterisation. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 173(1), 155-162. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1097(99)00065-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13497.x
Kalayu, G. (2019). Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms: Promising approach as biofertilizers. International Journal of Agronomy, Artículo 4917256. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4917256 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4917256
Kamal, T. S., Huang, Y., Xu, S., Islam, I., & Cui, S. (2019). Phosphorus demand for food security: A case study of a food-deficient country. Sustainability, 11(5), 1-18. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051345 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051345
Karam, D., Westra, P., Niessen, S. J., Ward, S. M., & Figueiredo, J. E. F. (2006). Assessment of silver-stained AFLP markers for studying DNA polymorphism in proso millet (Panicum miliaceum L.). Revista Brasileira de Botanica, 29(4), 609-615. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-84042006000400011 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-84042006000400011
Khan, M. S., Zaidi, A., & Ahmad, E. (2014). Mechanism of phosphate solubilization and physiological functions of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms. En M. S. Khan, A. Zaidi & J. Mussarrat (Eds.), Phosphate Solubilizing Microorganisms (pp. 34-35). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3=319-08216-5_2
King, E., Ward, M., & Raney, E. (1954). Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and luorescein. Journal of Laboratory Clinical Medicine, 44(2), 301-307.
Kruse, J., Abraham, M., Amelung, W., Baum, C., Bol, R., Kühn, O., Lewandowski, H., Niederberger, J., Oelmann, Y., Rüger, C., Santner, J., Siebers, M., Siebers, N., Spohn, M., Vestergren, J., Vogts, A., & Leinweber, P. (2015). Innovative methods in soil phosphorus research: A review. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 178(1), 43-88. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201400327 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201400327
Kuhad, R. C., SinghSurender, L., & Singh, A. (2011). Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. En A. Singh, N. Parmar & C. Kuhad (Eds.), Bioaugmentation, biostimulation, biocontrol, soil biology (pp. 65-84). Springer. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-19769-7_4
Kumar, V., & Narula, N. (1999). Solubilization of inorganic phosphates and growth emergence of wheat as affected by Azotobacter chroococcum mutants. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 28(3), 301-305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050497 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050497
Kumar, P., Mahesh, M., Yoganada, V., & Ammani, K. (2014). Molecular characterisation of Pseudomonas species isolated from diabetic patients with urinary tract infection (UTI) by AFLP. International Journal of Public Mental Health and Neurosciences, 1(1), 45-51. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-4709-1_5
Letunic, I & Bork, P. (2019). Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v4: recent updates and new developments. Nucleic acids research, 47 (W1), W256-W259. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz239. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz239
Liang, J. L., Liu, J., Jia, P., Yang, T. Tao, Zeng, Q. wei, Zhang, S. Chang, Liao, B., Shu, W. Sheng, & Li, J. Tian. (2020). Novel phosphate-solubilizing bacteria enhance soil phosphorus cycling following ecological restoration of land degraded by mining. ISME Journal, 14, 1600-1613. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-020-0632-4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-020-0632-4
Linu, M. S., Asok, A. K., Thampi, M., Sreekumar, J., & Jisha, M. S. (2019). Plant growth promoting traits of indigenous phosphate solubilizing Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from chilli (Capsicumannuum L.) rhizosphere. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 50(4), 444-457. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2019.1566469 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2019.1566469
Liu, L., Li, A., Chen, J., Su, Y., Li, Y., & Ma, S. (2018). Isolation of a phytase-producing bacterial strain from agricultural soil and its characterization and application as an effective eco-friendly phosphate solubilizing bioinoculant. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 49(8), 984-994. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2018.1448863 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2018.1448863
Liu, M., Sui, X., Hu, Y., & Feng, F. (2019). Microbial community structure and the relationship with soil carbon and nitrogen in an original Korean pine forest of Changbai Mountain, China. BMC Microbiology, 19(1), Artículo 218. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-019-1584-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-019-1584-6
Matos, A., Gomes, I., Nietsche, S., Xavier, A., Gomes, W., Dos Santos, J., & Pereira, M. (2017). Phosphate solubilization by endophytic bacteria isolated from banana trees. Anais Da Academia Brasileira de Ciências, 89(4), 2945-2955. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765201720160111 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765201720160111
McPherson, M. R., Wang, P., Marsh, E. L., Mitchell, R. B., & Schachtman, D. P. (2018). Isolation and analysis of microbial communities in soil, rhizosphere, and roots in perennial grass experiments. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 137, Artículo e57932. https://doi.org/10.3791/57932 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3791/57932
Meena, R. S., Kumar, S., Datta, R., Lal, R., Vijayakumar, V., Brtnicky, M., Sharma, M. P.,Yadav, G. S., Jhariya, M. K., Jangir, C. K., Pathan, S. I., Dokulilova, T., Pecina, V., & Marfo, T. D. (2020). Impact of agrochemicals on soil microbiota and management: A review. Land, 9(34), Artículo 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9020034 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/land9020034
Melenya, C., Logah, V., Aryee, D., Abubakari, A., Tuffour, H. O., & Yeboah, I. B. (2015). Sorption of phosphorus in soils in the semi deciduous forest zone of Ghana. Applied Research Journal, 1(3), 169-175.
Munir, I., Bano, A., & Faisal, M. (2019). Impact of phosphate solubilizing bacteria on wheat (Triticum aestivum) in the presence of pesticides. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 79(1), 29-37. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.172213 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.172213
Nautiyal, C. S. (1999). An effcient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Letters, 170, 265-270. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13383.x
Obrist-Farner, J., Brenner, M., Curtis, J. H., Kenney, W. F., & Salvinelli, C. (2019). Recent onset of eutrophication in Lake Izabal, the largest water body in Guatemala. Journal of Paleolimnology, 62(4), 359-372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-019-00091-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-019-00091-3
Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Agricultura y la Alimentación. (2019). World fertilizer trends and outlook to 2022. Rome.
Oteino, N., Lally, R. D., Kiwanuka, S., Lloyd, A., Ryan, D., Germaine, K. J., & Dowling, D. N. (2015). Plant growth promotion induced by phosphate solubilizing endophytic Pseudomonas isolates. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6, Artículo 745. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00745 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00745
Patil, I. (2021). Visualizations with statistical details: The 'ggstatsplot' approach. Journal of Open Source Software, 6(61), 3167. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03167 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03167
Patiño-Torres, C., & Sánchez de Prager, M. (2012). Aislamiento e identificación de bacterias solubilizadoras de fosfatos, habitantes de la rizósfera de Chontaduro (B. gassipaes kunth). Biotecnología en el Sector Agropecuario y Agroindustrial, 10(2), 177-187.
Pérez-Álvarez, S., Coto-Arbelo, O., Echemendía-Pérez, M., & Ávila-Quezada, G. (2015). Pseudomonas fluorescens Migula, ¿control biológico o patógeno? Revista Protección Vegetal, 30(3), 225-234.
Pérez-Reynoso, J. R. (2008). Estudio de la concentración de cobre, zinc y manganeso en los suelos hortícolas del valle de San Pedro Almolonga, Quetzaltenango, sometidos a una agricultura intensiva [Tesis de licenciatura, Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala]. http://biblioteca.usac.edu.gt/tesis/01/01_2441.pdf
Porras, M., Barrau, C., Santos, B., Arroyo, F. T., Blanco, C., & Romero, F. (2002). Effects of temperature on in vitro response of Trichoderma strains against strawberry pathogen Rhizoctonia solani Kühn. Plant Protection Science, 38(SI 2), 620-622. https://doi.org/10.17221/10572-pps DOI: https://doi.org/10.17221/10572-PPS
R Core Team. (2020). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/.
Qessaoui, R., Bouharroud, R., Furze, J. N., El Aalaoui, M., Akroud, H., Amarraque, A., Vaerenbergh, J. Van, Tahzima, R., Mayad, E. H., & Chebli, B. (2019). Applications of new rhizobacteria Pseudomonas isolates in agroecology via fundamental processes complementing plant growth. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49216-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49216-8
Rahman, C. H., Miloud, B., Rachid, D., Ahcene, B., & Hakim, H. (2017). Optimization of inorganic phosphate solubilization by Pseudomonas fluorescens and Bacillus sp. isolated from wheat rhizospheric soil. International Journal of Biosciences, 10(4), 142-150. https://doi.org/10.12692/ijb/10.4.142-150 DOI: https://doi.org/10.12692/ijb/10.4.142-150
Redel, Y., Rubio, R., Rouanet, J. L., & Borie, F. (2007). Phosphorus biavailability affected by tillage and crop rotation on a Chilean volcanic derived ultisol. Geoderma, 139, 388-396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.02.018 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.02.018
Rejmánková, E., Komárek, J., Dix, M., Komárková, J., & Girón, N. (2011). Cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Atitlan, Guatemala. Limnologica, 41(4), 296-302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2010.12.003 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2010.12.003
Restrepo-Franco, G. M., Marulanda-Moreno, S., de la Fe-Pérez, Y., Díaz-de la Osa, A., Lucia-Baldani, V., & Hernández-Rodríguez, A. (2015). Bacterias solubilizadoras de fosfato y sus potencialidades de uso en la promoción del crecimiento de cultivos de importancia económica. Revista CENIC Ciencias Biologicas, 46(1), 63-76.
Richardson, A. E., Barea, J. M., McNeill, A. M., & Prigent-Combaret, C. (2009). Acquisition of phosphorus and nitrogen in the rhizosphere and plant growth promotion by microorganisms. Plant and Soil, 321(1-2), 305–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-9895-2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-9895-2
Richardson, A. E., & Simpson, R. J. (2011). Soil microorganisms mediating phosphorus availability. Plant Physiology, 156, 989-996 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.175448
Ryan, P. D., Hammer, Ø., & Harper, D. A. (2001). Past: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontologia Electronica, 4(1), 5-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2008.05.025 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2008.05.025
Saitou, N., & Nei, M. (1987). The neighbour-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution Biol Evo, 4(4), 406-425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Sarikhani, M. R., Aliasgharzad, N., & Khoshru, B. (2020). P solubilizing potential of some plant growth promoting bacteria used as ingredient in phosphatic biofertilizers with emphasis on growth promotion of Zea mays L. Geomicrobiology Journal, 37(4), 327-335. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2019.1700323 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2019.1700323
Scarpellini, M., Franzetti, L., & Galli, A. (2004). Development of PCR assay to identify Pseudomonas fluorescens and its biotype. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 236(2), 257-260. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2004.tb09655.x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2004.tb09655.x
Sharma, K. (2011). Inorganic phosphate solubilization by fungi isolated from agriculture soil. Journal of Phytology, 3(4), 11-12.
Shen, J., Yuan, L., Zhang, J., Li, H., Bai, Z., Chen, X., Zhang, W., & Zhang, F. (2011). Phosphorus dynamics: From soil to plant. Plant Physiology, 156(3), 997-1005. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.175232 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.175232
Situmorang, E. C., Prameswara, A., Sinthya, H. C., Toruan-Mathius, N., & Liwang, T. (2015). Indigenous phosphate solubilizing bacteria from peat soil for an eco-friendly biofertilizer in oil palm plantation. KnE Energy, 1(1), 65-72. https://doi.org/10.18502/ken.v1i1.324 DOI: https://doi.org/10.18502/ken.v1i1.324
Smith, T. P., Thomas, T. J. H., García-Carreras, B., Sal, S., Yvon-Durocher, G., Bell, T., & Pawar, S. (2019). Community-level respiration of prokaryotic microbes may rise with global warming. Nature Communications, 10(1), Artículo 5124. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13109-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13109-1
Suleman, M., Yasmin, S., Rasul, M., Yahya, M., Manzoor, B., & Mirza, M. (2018). Phosphate solubilizing bacteria with glucose dehydrogenase gene for phosphorus uptake and beneficial effects on wheat. PLoS ONE, 13(9), Artículo e0204408. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204408 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204408
Tak, H. I., Ahmad, F., Babalola, O. O., & Inam, A. (2012). Growth, photosynthesis and yield of chickpea as influenced by urban wastewater and different levels of phosphorus. International Journal of Plant Research, 2, 6-13. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.plant.20120202.02 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5923/j.plant.20120202.02
Velásquez, G., Calabi-Floody, M., Poblete-Grant, P., Rumpel, C., Demanet, R., Condron, L., & Mora, M. L. (2016). Fertilizer effects on phosphorus fractions and organic matter in Andisols. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 16(2), 294-309. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162016005000024 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162016005000024
Vos, P., Hogers, R., Bleeker, M., Reijans, M., van de Lee, T., Hornes, M., Friters, A., Pot, J., Paleman, J., Kuiper. (1995). AFLP: A new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Research, 23(21), 4407-4414. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/23.21.4407 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/23.21.4407
Wang, Z., Liu, Y., Zhao, L., Zhang, W., & Liu, L. (2019). Change of soil microbial community under long-term fertilization in a reclaimed sandy agricultural ecosystem. PeerJ, 7, Artículo e6497. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6497 DOI: https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6497
Yadav, A., Yadav, K., & Vashistha, A. (2016). Phosphate solubilizing activity of Pseudomonas fluorescens PSM1 isolated from wheat rhizosphere. Journal of Applied and Natural Science, 8(1), 93-96. https://doi.org/10.31018/jans.v8i1.754 DOI: https://doi.org/10.31018/jans.v8i1.754
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Jose A. Ruiz-Chutan, Julio E. Berdúo-Sandoval, Anibal Sacbajá, Marie Kalousová, Bohdan Lojka, Eloy Fernandez, Jana Žiarovská, Amilcar Sanchez-Perez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
El autor que publique en esta revista acepta las siguientes condiciones:
- El autor otorga a la Dirección General de Investigación el derecho de editar, reproducir, publicar y difundir el manuscrito en forma impresa o electrónica en la revista Ciencia, Tecnología y Salud.
- La Direción General de Investigación otorgará a la obra una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0 Internacional









